ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ
ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਓਹ ਢਾਂਚੇ ਜਾਂ ਰਚਨਾ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਸਦਾ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਤਲ ਤਿਕੋਣੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਚੋਟੀ ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਬਿੰਦੁ ਤੇ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਕਾਰਣ ਇਸਦੀ ਆਕ੍ਰਿਤੀ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਵਰਗੀ ਜਿਆਮਿਤੀ ਦੀ ਤਰਾਂ ਹੈ। ਇਸਦਾ ਤਲਾ ਤ੍ਰੈਬਾਹੀ, ਚੁਬਾਹੀਆ ਜਾਂ ਬਹੁਭੁਜ ਆਕਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ। ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਆਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਰਚਨਾਂਵਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾ ਇਹ ਹੈ ਕੀ ਇਸਦੇ ਭਾਰ ਦਾ ਅੰਸ਼ ਜ਼ਮੀਨ ਦੇ ਕੋਲ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਕਾਰਣ ਪੁਰਾਤਨ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾਂਵਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸ ਵੰਡ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਇਮਾਰਤਾਂ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਵਰਤਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ। ਵਿਸ਼ਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਸੰਰਚਨਾਂਵਾਂ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਦੀ ਆਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਹੇਨ ਜਿੰਨਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਸਰ ਦੇ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਬਹੁਤ ਪ੍ਰਸਿਧ ਹੈ। ਮਿਸਰ ਦੇ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਉੱਥੋਂ ਦੇ ਸਮਰਾਟਾਂ ਦੇ ਮ੍ਰਿਤਕ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਰੱਖਣ ਲਈ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ। ਮਿਸਰ ਵਿੱਚ 138 ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਹਨ, ਪਰ ਸਿਰਫ਼ ਗੀਜ਼ਾ ਦਾ ਗ੍ਰੇਟ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਹੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਵਿਸ਼ਵ ਦੇ 7 ਅਜੂਬਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸੂਚੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਕਰੀਬ 2560 ਸਾਲ ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਮਿਸਰ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ ਖ਼ੁਫ਼ੂ ਦੇ ਚੌਥੇ ਵੰਸ਼ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਆਪਣੀ ਕਬਰ ਦੇ ਤੌਰ ’ਤੇ ਕਰਵਾਿੲਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਰੀਬ 25 ਸਾਲ ਲੱਗੇ ਸਨ। ਇਸ ਦੀ ਲੰਬਾਈ 450 ਫੁੱਟ ਹੈ। ਜ਼ਮੀਨ ’ਤੇ ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਘੇਰਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਖੇਤਰਫਲ 16 ਫੁੱਟਬਾਲ ਦੇ ਮੈਦਾਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਨੂੰ 25 ਲੱਖ ਚੂਨਾ ਪੱਥਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਖੰਡਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਿਗਆ ਹੈ। ਵਿਗਿਆਨੀ ਹੁਣ ਤਕ ਇਹ ਨਹੀਂ ਸਮਝ ਸਕੇ ਕਿ ਐਨੇ ਵੱਡੇ ਪੱਥਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ 450 ਫੁੱਟ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਾਈ ਤਕ ਕਿਵੇਂ ਲਿਜਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ਇਹ ਵੀ ਇੱਕ ਹੈਰਾਨੀ ਵਾਲਾ ਤੱਥ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਸਿਰਫ਼ 30 ਸਾਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਿਕਵੇਂ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਅਜਿਹੀ ਸੰਰਚਨਾ ਬਣਾਉਣੀ ਮੁਸ਼ਕਲ ਸੀ।

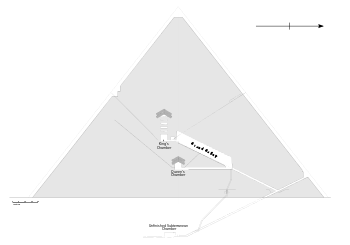
ਬਣਾਵਟ ਦੀ ਤਕਨੀਕਾਂ
ਸੋਧੋਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਨੂੰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੱਥਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਢੋਆ-ਢੁਆਈ ਕਰਨੀ ਪੈਂਦੀ ਹੈ। ਪੱਥਰ ਜਾਂ ਬਲਾਕ ਇੱਕ ਥਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਦੂਜੀ ਥਾਂ ਲੱਕੜ ਦੀ ਰੇੜੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਸੀ। ਢੁਆਈ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਰੇਤ ਨੂੰ ਗਿੱਲਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਰੇਤ ਕੱਠੀ ਹੋਕੇ ਚਿਪਕ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਤੇ ਭਾਰੀ ਪੱਥਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਰੇੜੀ ਤੇ ਢੁਆਈ ਕਰਨੀ ਸੌਖੀ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਸੀ।[1][2]
ਮਿਸਰ ਦੇ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ
ਸੋਧੋਮਿਸਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਾਜੇ ਤੇ ਰਾਣੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਫ਼ਿਰਔਨ(pharaoh) ਆਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ ਜੋ ਕੀ ਪਥਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਬਣੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਫ਼ਨਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਸੀ। ਤੇ ਇੰਨਾ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਵ ਨੂੰ ਮਮੀ ਆਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇੰਨਾ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਖਾਣ-ਪੀਣ ਦਾ ਸਮਾਨ, ਕਪੜੇ, ਗਹਿਣੇ, ਬਰਤਨ, ਹਥਿਆਰ, ਜਾਨਵਰ, ਤੇ ਕਦੇ ਕਦੇ ਤਾਂ ਸੇਵਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਨਾਲ ਹੀ ਦਫ਼ਨਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ। ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਫ਼ਿਰਔਨ ਮਕਬਰੇ ਲਈ ਖਾਸ ਤੌਰ ਤੇ ਬਨਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਸੀ ਜੋ ਕੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਸੀ ਤੇ ਅੱਜ ਵੀ ਮੌਜੂਤ ਹਨ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਤਰਾਂ ਮਿਸਰ ਦੀ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾਂ ਵੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਪੁਰਾਣੀ ਹੈ। ਮਿਸਰ ਵਿੱਚ 138 ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਹਨ। ਸਬਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਸਟੈਪ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਕੀ ਕਾਇਰੋ, ਮਿਸਰ ਦੇ ਕੋਲ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਸਮਰਾਟ ਦਜੋਸਰ ਲਈ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾਂ ਸਾਲ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ਉਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਦ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਵੱਡੇ ਆਕਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਣਨ ਲੱਗ ਪਏ। ਸਬਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਗੀਜ਼ਾ ਦਾ "ਗ੍ਰੇਟ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ" ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਕਾਇਰੋ ਦੇ ਨਜ਼ਦੀਕ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਫ਼ਿਰਔਨ ਖ਼ੁਫ਼ੂ ਨੇ ਬਣਵਾਇਆ ਸੀ। ਇਸਨੂੰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਵੀਹ ਸਾਲ ਲੱਗ ਗਏ ਸੀ। ਗੀਜ਼ਾ ਦਾ ਇਹ ਪੁਰਾਤਨ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਦੁਨਿਆ ਦੇ ਸੱਤ ਅਚੰਭੇ ਦੀ ਸੂਚੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੌਜੂਦ ਹੈ। ਦੁਨਿਆ ਦੇ ਪੁਰਾਣੇ ਸੱਤ ਅਚੰਭੇ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਸਿਰਫ ਇੱਕ ਇਹੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਨੂੰ ਕਾਲ ਨੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਿਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਿੱਤਾ ਹੈ। ਲੋਕ ਸੋਚਦੇ ਸੀ ਕੀ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਗੁਲਾਮਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਬਣਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਸੀ ਪਰ ਹਾਲ ਹੀ ਦੇ ਸਬੂਤ ਸੁਝਾਅ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਕੀ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਮਜ਼ਦੂਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਖੂਬ ਸੇਵਾ ਕਿੱਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਤੇ ਦੌਲੱਤ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਿੱਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਸੀ। ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਵਿੱਚ ਚੋਰਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਖ਼ਜ਼ਾਨੇ ਨੂੰ ਬਚਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਕੁੜਿੱਕੀ ਜਾਂ ਫੰਦੇ ਲਗਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਸੀ ਤੇ ਜੇ ਕੋਈ ਚੋਰ ਪਕੜਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਤਾਂ ਉਸਨੂੰ ਮੌਤ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਸੀ। ਇੱਕ ਹਜ਼ਾਰ ਈਸਵੀ ਪੂਰਵ ਤੱਕ ਤਕਰੀਬਨ ਸਾਰੇ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਖ਼ਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਚੋਰੀ ਹੋ ਚੁੱਕਿਆ ਹੈ। ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਮਿਸਰੀ ਮੰਨਦੇ ਸੀ ਕੀ ਮਿਸਰੀ ਫ਼ਿਰਔਨ ਦੀ ਆਤਮਾ ਨੂੰ ਸਵਰਗ ਪਹੂੰਚਾਣ ਲਈ ਪਿਰਾਮਿਡ ਇੱਕ ਤਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਸੀੜ੍ਹੀ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੇ ਸੀ।
| Pharaoh | Ancient name | Dynasty | Site | Base length x Height (m) | Volume (cu.m) | Inclination & Notes | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Djoser | ancient name: unknown modern name: Step Pyramid of Djoser |
3rd (c. 2686 – 2613 BC) |
Saqqara | 121w.x109d.x60h. | 330,400 | [3] | |
| Sekhemkhet | ancient name: unknown modern name: Buried Pyramid |
3rd | Saqqara | 120sq.x7h. | 33,600 (unfinished) | [4] | |
| Khaba (uncertain) |
ancient name: unknown modern name: Layer Pyramid |
3rd | Zawyet el'Aryan | 84sq.x20h. | 47,040 (unfinished) | [5] | |
| Sneferu | ancient name: Snefru endures modern name: Pyramid of Meidum |
4th | Meidum | 144sq.x92h. | 638,733 | 51° 50' 35"[6] | |
| Sneferu | ancient name: Snefru shines in the South modern name: Bent Pyramid |
4th | Dahshur | 188sq.x105h. | 1,237,040 | 54° 50' 35" /43° 22'[6] | |
| Sneferu | ancient name: Snefru shines in the North modern name: Red Pyramid |
4th | Dahshur | 220sq.x105h. | 1,694,000 | 43° 22'[7] | |
| Khufu | ancient name: Khufu's horizon modern name: The Great Pyramid of Giza |
4th | Giza | 230.3sq.x146.6h. | 2,583,283 | 51° 50' 40"[8] | |
| Djedefre | ancient name: Star tent of Djedefre modern name: Pyramid of Djedefre |
4th | Abu Rawash | 106.2sq.x~68h.[9] | 131,043 | ~52°[6][9] | |
| Bikheris? Seth-Ka?[10] |
ancient name: Star of ..?..-Ka modern name: Unfinished Northern Pyramid of Zawyet el'Aryan |
4th (uncertain) |
Zawyet el'Aryan | 200sq.x140h.[11] | [12] | ||
| Khafra | ancient name: Khafra is great modern name: Khafre's Pyramid |
4th | Giza | 215.25sq.x143.5h. | 2,211,096 | 53°10'[6] | |
| Menkaure | ancient name: Menkaure is godlike modern name: Menkaure's Pyramid |
4th | Giza | 103.4sq.x65.5h. | 235,183 | 51°20′25″[13] | |
| Userkaf | ancient name: The pure sites of Userkaf modern name: Pyramid of Userkaf |
5th (c. 2498 – 2345 BC) |
Saqqara | 73.3sq.x49h. | 87,906 | 53°7'48"[6] | |
| Sahure | ancient name: The soul of Sahure appears modern name: Pyramid of Sahure |
5th | Abusir | 78.75sq.x47h. | 96,542 | 50°11'40"[6] | |
| Neferirkare Kakai | ancient name: Soul of Neferirkare modern name: Pyramid of Neferirkare |
5th | Abusir | 105sq.x54h. | 257,250 | 54°30'[14] | |
| Neferefre | ancient name: Thr power of Neferefre is godlike modern name: Pyramid of Neferefre |
5th | Abusir | 65sq.x?h. | (unfinished) | ||
| Niuserre | ancient name: The seats of Niuserre will endure modern name: Pyramid of Niuserre |
5th | Abusir | 79.9sq.x51.68h. | 112,632 | 51° 50' 35"[15] | |
| Menkauhor Kaiu(?)[16] | ancient name: unknown modern name: Headless Pyramid |
5th | Saqqara | c.52sq.x?h. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| Djedkare Isesi | ancient name: Beauty of Isesi modern name: Pyramid of Djedkare-Isesi |
5th | South Saqqara | 78.75sq.x52.5h. | c.107,835 | 52°[17] | |
| Unas | ancient name: The seats of Unas are beautiful modern name: Pyramid of Unas |
5th | North Saqqara | 57.75sq.x43h. | 47,390 | 56°[6] | |
| Teti | ancient name: The seats of Teti are eternal modern name: Pyramid of Teti |
6th (c. 2345 – 2181 BC) |
North Saqqara | 78.5sq.x52.5h. | 107,835 | 53° 7' 48"[18] | |
| Pepi I | ancient name: The beauty of Pepi may endure modern name: Pyramid of Pepi I |
6th | South Saqqara | 78.75sq.x52.5h. | c. 107,835 | 53° 7' 48"[19] | |
| Merenre | ancient name: The beauty of Merenre appears modern name: Pyramid of Merenre |
6th | South Saqqara | 78.75sq.x52.5h. | c. 107,835 | 57°7'48" | |
| Pepi II | ancient name: Pepi is established and living modern name: Pyramid of Pepi II |
6th | South Saqqara | 78.75sq.x52.5h. | c.107,835 | 53° 7' 48"[8] | |
| Qakare Ibi | ancient name: unknown modern name: Pyramid of Ibi |
8th | South Saqqara | 31.5sq.x21?h. | 6,994? | 53° 7′[20] | |
| Khui | ancient name: unknown modern name: Pyramid of Khui |
First Intermediate Period | Dara | 146w.x136d.x?h. | n.d. | n.d.[21] | |
| Merikare | ancient name: Flourishing are the abodes of Merikare modern name: Pyramid of Merikare |
10th | Unknown, possibly North Saqqara | n.d. | n.d. | n.d.[22] | |
| Amenemhat I | ancient name: Amenemhat appears at his place modern name: Pyramid of Amenemhet I |
12th (c. 1991 – 1803 BC) |
Lisht | 84sq.x55h. | 129,360 | 54° 27' 44" | |
| Senusret I | ancient name: Senusret beholds the two lands modern name: Pyramid of Senusret I |
12th | Lisht | 105sq.x61.25h. | 225,093 | 49° 24'[23] | |
| Amenemhat II | ancient name: Amenemhat is provided modern name: White Pyramid |
12th | Dashur | 50sq.x?h. | |||
| Senusret II | ancient name: Senusret appears modern name: Pyramid of Senusret II |
12th | Illahun (El-Lahun) | 106sq.x48.6h. | 185.665 | 42° 35'[24] | |
| Senusret III | ancient name: unknown modern name: Pyramid of Senusret III |
12th | Dashur | 105sq.x78h. | 288,488 | 56° 18' 35"[25] | |
| Amenemhat III | ancient name: Amenemhat is beautiful modern name: Pyramid of Amenemhat III |
12th | Dashur | 105sq.x75h. | 274,625 | 56° 18' 35" | |
| Amenemhat III | ancient name: Amenemhat lives modern name: Pyramid of Hawara |
12th | Hawara | 105sq.xc. 58h. | 200,158 | 48° 45' | |
| Amenemhat IV (?) | ancient name: unknown modern name: Southern Mazghuna pyramid |
12th or 13th | South Mazghuna | 52.5sq.x?h.(unfinished) | n.d. | n.d. | |
| Sobekneferu (?) | ancient name: unknown modern name: Northern Mazghuna pyramid |
12th or 13th | North Mazghuna | > 52.5sq.x?h.(unfinished) | n.d. | n.d. | |
| Ameny Qemau | ancient name: unknown modern name: Pyramid of Ameny Qemau |
13th (c. 1790 BC) |
South Saqqara | 52sq.x c. 35h. | c 55° | ||
| Khendjer | ancient name: unknown modern name: Pyramid of Khendjer |
13th (c. 1760 BC) |
South Saqqara | 52.5sq.x c. 37.35h. | c. 34,300 | 55°[26] | |
| unknown | ancient name: unknown modern name: Southern South Saqqara pyramid |
13th | South Saqqara | 78.75sq.x?h.(unfinished) | n.d. | n.d. | |
| Ahmose I | ancient name: unknown modern name: Pyramid of Ahmose |
18th (c. 1550 – 1292 BC) |
Abydos | 52.5sq.x c. 10h. | 60°[27] |
ਗੈਲਰੀ
ਸੋਧੋ-
Pyramid of Khafra
-
Prasat Thom temple at Koh Ker
-
Stockport Pyramid in Stockport, United Kingdom
-
Karlsruhe Pyramid, Germany
-
The Pyramid Arena in Memphis, Tennessee
-
Hanoi Museum in Vietnam features an overall design of a reversed Pyramid.
-
Metairie Cemetery, New Orleans
-
Pyramidal road church in Baden-Baden, Germany
-
Pyramid Arena in Memphis, Tennessee
-
Oscar Niemeyer's design for a museum in Caracas
-
Transamerica Pyramid in San Francisco, California
-
Pyramid of Cestius in Rome
-
A diagram showing the various components of Eastern North American platform mounds
-
Chogha Zanbil is an ancient Elamite complex in the Khuzestan province of Iran.
ਹਵਾਲੇ
ਸੋਧੋ- ↑ "ਪੁਰਾਲੇਖ ਕੀਤੀ ਕਾਪੀ". Archived from the original on 2016-04-09. Retrieved 2014-12-17.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ Terrence McCoy (2014-05-02). "The surprisingly simple way Egyptians moved massive pyramid stones without modern technology". Washington Post.
- ↑ The pyramid complex covers 37 acres (150,000 m2) and provides several cultic buildings. It is one of the best preserved Old Kingdom royal cemeteries and hides several, huge underground mazes of niched corridors and chambers.
- ↑ Rediscovered in 1951 by Zakaria Goneim. Famous for its sarcophagus made of alabaster, which was found in situ and sealed. Surprisingly, the sarcophagus was empty and possibly never in use.
- ↑ The connection to king Khaba is disputed, since not a single artifact with any royal name was found in the underground chambers.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid.
- ↑ First true pyramid.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid and 3 queens pyramids.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Vallogia, Michel (University of Geneva), Joanne Rowlands (University of Oxford), and Dr Zahi Hawass (Secretary General of the Egyptian Supreme Council of Antiquities) (2008-06-23). The Lost Pyramid (Television documentary). History. Retrieved 2008-12-12.
- ↑ For the problematic, see: Jürgen von Beckerath: Chronologie des pharaonischen Ägypten. Die Zeitbestimmung der ägyptischen Geschichte von der Vorzeit bis 332 v. Chr. (= Münchner ägyptologische Studien, vol. 46). von Zabern, Mainz 1997, ISBN 3-8053-2310-7, page 158.
- ↑ Rainer Stadelmann: Die Ägyptischen Pyramiden: vom Ziegelbau zum Weltwunder (= Kulturgeschichte der antiken Welt, vol. 30). von Zabern, Mainz 185, ISBN 3805308558, p. 77, 140-145.
- ↑ Six ink inscriptions once contained a cartouche name, which remains illegible. There are dozens of different readings proposed by Egyptologists. See: Miroslav Verner: Archaeological Remarks on the 4th and 5th Dynasty Chronology. In: Archiv Orientální, vol. 69. Praha 2001, page 363–418.
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes 3 queens pyramids.
- ↑ Originally built a stepped pyramid.
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid and 1 or 2 queens pyramids.
- ↑ Reuters: Jonathan Wright: Eroded pyramid attributed to early pharaoh, June 5, 2008
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid and 1 queens pyramid.
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid and 2 queens pyramids.
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid and 5 queens pyramids.
- ↑ Last pyramid built in Saqqara.
- ↑ Unclear if it was a step pyramid or a giant mastaba.
- ↑ Archaeologically attested, but still unidentified.
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid and 9 queens pyramids.
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid or a queens pyramid.
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes 7 queens pyramids.
- ↑ Pyramid complex includes a satellite pyramid and two enclosure walls.
- ↑ Built as a Cenotaph. It is the only royal pyramid in Abydos.
| ਇਹ ਲੇਖ ਅਧਾਰ ਹੈ। ਤੁਸੀਂ ਇਸਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਕੇ ਵਿਕੀਪੀਡੀਆ ਦੀ ਮੱਦਦ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ। |